Private Cloud is a type of Cloud Computing deployment model, where the underlying hardware infrastructure and software are exclusively used by an entity. (a single company or a single organization).
The private cloud can either be directly owned and operated by an entity or it can be hosted by a third party service provider.
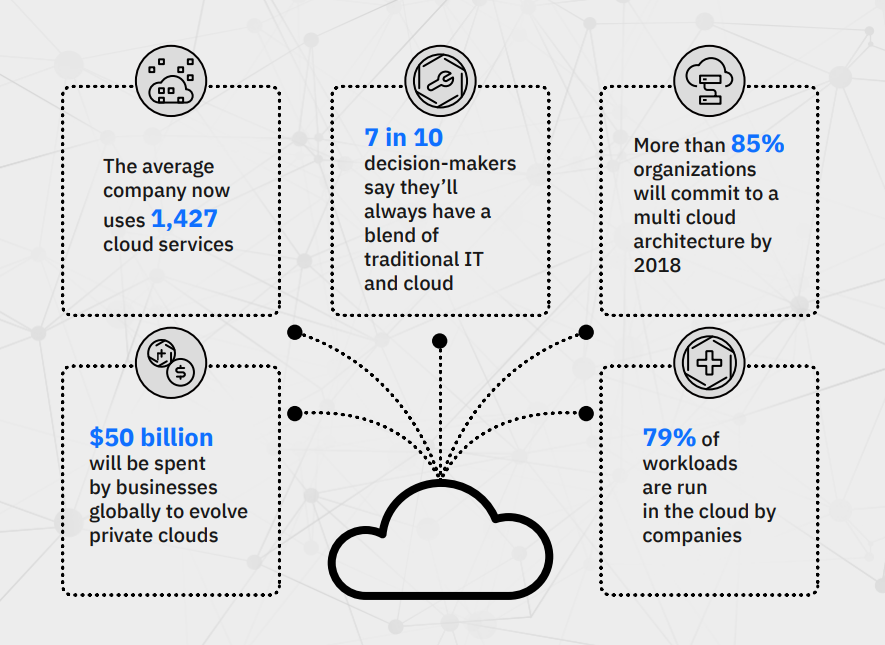
Examples:
Directly owned and operated: With more than two billion monthly active users, Facebook’s data requirements are as big as it can get. To serve billions of people every day, Facebook has deployed a massive infrastructure across the world, a scalable private cloud of its own.
Third-party hosted: Amazon Virtual Private cloud allows users to build a logically isolated section in the cloud. Users can launch all their resources in a virtual network that’s completely under their control. Customers who want their operations to be isolated from others can buy dedicated AWS infrastructure, which means the hardware can only be used by them.
Private Cloud vs Public Cloud
In a public cloud, a third-party provider such as AWS, Microsoft Azure or Google Cloud owns and maintains the software and hardware infrastructure. Customers rent the infrastructure and other services on demand. More often than not customers will be sharing the underlying resource with others, hence the name public cloud.
In a private cloud, you either own the infrastructure or you are given exclusive access to the infrastructure.
Advantages of a private cloud:
-
Flexibility: The cloud environment can be completely customized to serve the needs your business.
-
Scalability: If the private cloud is hosted by a cloud service provider, you get the ability to instantly scale your resources up or down.
-
Added security: Since your resources are isolated and not shared with other customers, the private cloud offers higher control over the environment and increases security
-
Compliance: Achieving compliance will be easier as the operational environment is completely under your control. Companies that operate in data-sensitive industries are better off in a private cloud.
-
Best of both worlds: Private cloud gives you the best of both worlds. You get increased security, but still, retain the scalability and efficiency of public clouds.
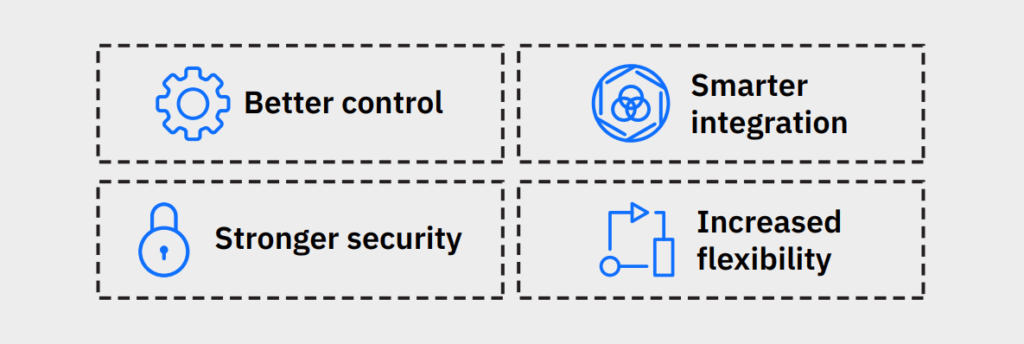
Disadvantages of Private Cloud
-
Expensive: A private cloud will cost you a lot more than a public cloud. Dedicated resources are expensive to rent. If you own the infrastructure, you will have to buy, manage and maintain it, which makes it costlier than operating a public cloud, where the infrastructure is owned and operated by the third party.
-
Optimization: Capacity planning will remain a huge challenge as resources can often be underutilized.
-
Complexity: Though private clouds offer several advantages, they can be extremely complex to maintain.
-
Talent: You will need workers with a specialized skill set to run your private cloud. This can further increase the cost of running a private cloud.
Understanding the Private Cloud: An Explanation from IBM
For most, the cloud represents accessing and consuming someone else’s compute resources. Images of a team of minions and automation quickly come to mind. While you no longer control the environment, you can now dynamically provision and access compute resources to build, test and scale all manner of applications and services.
But what happens when you can’t give up control for strategic or regulatory reasons? Many organizations are grappling with the need to work faster, deliver sooner, and scale infinitely but, in many cases, cannot run their applications on the public cloud.
Most of the time they are held back by regulatory and legal requirements. Others do not want their strategic assets to leave their organization.
Does this mean that organizations with sensitive or strategic applications will lose out on the benefits of a cloud architecture? No. We believe a Private cloud can bring the benefits of a public cloud behind your firewall.
A private cloud is like a fenced-in backyard with a gate to surrounding properties and public spaces. It can give you many of the benefits of a public cloud with the additional control and security of dedicated resources.
Introduction to IBM Cloud Private