Cloud computing is the on-demand delivery of various types of technology solutions delivered over the internet. That includes computing power, storage services, software development platforms, software applications and other IT-related services.
In its simplest form, cloud computing is the outsourcing of technology infrastructure and related functionalities to a third party company in order to reduce overheads and minimize the need for in-house resources.
Cloud Service Providers (CSPs) typically offer a range of services that may include all or some of these: Access to servers, development platforms, storage solutions, databases and applications.
What are the Different Components of Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is broadly divided into three categories:
- Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS)
- Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS)
- Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
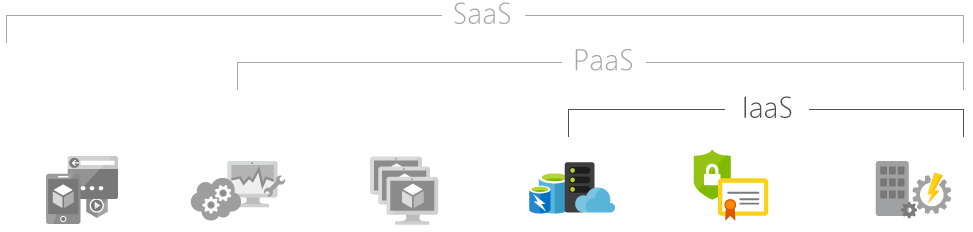
Image Source: Microsoft
Definition of Infrastructure-as-a-Service – What is IaaS?
Infrastructure-as-a-Service, or IaaS, is the first layer of cloud. IaaS provides on-demand computing infrastructure that can be provisioned and managed over the internet.
IaaS is made up of three essential building blocks: Servers, Storage and Network. Everything else that goes into IaaS is built as overlayers on top of this skeletal structure. These layers typically bring efficiency, scalability and other benefits that make IaaS an ideal alternative to traditional, in-house IT infrastructure.
A good analogy would be what you’d see in a personal computer. The same three things would apply: compute power or processor power and speed, storage availability and connectivity.
Definition of Platform-as-a-Service – What is PaaS?
Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) is an on-demand environment provided to the consumer for developing, testing, delivering and managing software applications.
It removes the need for organizations to manage their own infrastructure that includes networks, servers, operating systems and storage, allowing them to focus on the development, deployment and management of their applications.
“(A PaaS) provider offers access to a cloud-based environment in which users can build and deliver applications. The provider supplies underlying infrastructure.” – IBM
Definition of Software-as-a-Service – What is SaaS?
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) is the on-demand delivery of software applications over the Internet. The SaaS provider runs and manages the service, taking care of the underlying infrastructure, while the end user, or the subscriber of the service, accesses it through the web or vendor API’s. Web based e-mail is the most commonly used SaaS application.
SaaS is usually the topmost layer, hosting applications on the cloud and serving or delivering them using the Internet. This is the part that most of us know but may not even be aware of. Your Gmail, your Facebook, your Spotify and your Internet banking portal – all of these are SaaS applications, or software provided as a service over the internet. Whenever you access an application on the web that doesn’t require you to download anything, that’s a SaaS application.
What are the Different Models of Cloud Computing Deployment?
- Public Cloud
- Hybrid Cloud
- On-Premises
Definition of Public Cloud – What is Public Cloud?
Public Cloud is a type of cloud deployment where a CSP’s resources are shared between several clients. It is a dynamic environment where virtual “instances”, or virtual machines (VMs) are used to run the client’s applications, which are then served to customers.
It is the most common type of cloud deployment, and requires little more than an internet connection. Communication with the virtual servers happens via the Internet, and can be set up with different types of authentications and other security measures.
Just as your computer’s data is protected by firewalls, anti-virus software, passwords and other forms of authentication, public cloud environments are also protected in a similar manner.
Today, enterprise-level security is often mandatory, and critical to the success of any CSP. Not many companies will put their workloads on public cloud if they aren’t assured of the highest levels of security for their data.
In the United States, the Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program – or FedRAMP – is one such accreditation. A “high impact level” accreditation from FedRAMP means that the cloud environment is secure enough to hold “Personally Identifiable Information (PII), sensitive patient records, financial data, law enforcement data, and other Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI).”
Public cloud is typically offered on a pay-as-you-go basis. Instances are normally charged on a per-hour rate, while storage is charged at a per-GB rate. Several factors impact the pricing, such as the type of instance required, whether or not dedicated physical servers are required and so on.
Definition of Hybrid Cloud – What is Hybrid Cloud?
The third mode of deployment is hybrid cloud, and it takes the best elements of on-prem and public cloud to create a blended model, with client’s and provider’s resources working side by side to accomplish much more than what the client’s resources alone can do. As a flexible model, it gives the client more control over where the data is stored, what gets put on the cloud and so on.
Many large enterprises have found that it is easier to maintain portions of their existing infrastructure, while leveraging the scalability and flexibility of public cloud. As a result, hybrid managed cloud is emerging as the most preferred type of cloud deployment in the industry.
Definition of On-Premises Cloud – What is Private Cloud?
On-premises, also referred to as just on-prem, indicates that the resources, such as physical servers, are located at the client’s facilities. An on-premise cloud, also known as Private Cloud or Managed Cloud, involves primary resources taken from the client, but managed as a cloud environment by a CSP, usually with proprietary architecture.
Private Cloud solutions are generally preferred by companies whose prime objective is the security of the data they hold. Financial institutions, government entities and other such organizations usually prefer to maintain their own infrastructure but still have it operate like a flexible cloud environment.
The State of Cloud Computing: Historical Growth, Current Status and Future Growth Projections
In 2019, Worldwide Public Cloud spending is forecast to hit $206.2 billion revenue, up from $175.8 billion in 2018, growth of 17.2%. Data from Gartner shows that Software-as-a-Service segment will account for nearly half the industry’s growth in 2019.

Cisco Global Cloud Index: 2016 to 2021
-
Hyperscale data centers will grow from 338 in number at the end of 2016 to 628 by 2021.
-
73 percent of the cloud workloads and compute instances will be in public cloud data centers, up from 58 percent in 2016 (CAGR of 27.5 percent from 2016 to 2021).
-
75 percent of the total cloud workloads and compute instances will be Software-as-a-Service (SaaS), up from 71 percent in 2016.
-
16 percent of the total cloud workloads and compute instances will be Infrastructure-as-a-Service(IaaS), down from 21 percent in 2016.
Gartner:
-
By 2022, Gartner expects that 90 percent of organizations purchasing public cloud IaaS will do so from an integrated IaaS and platform as a service (PaaS) provider, and will use both the IaaS and PaaS capabilities from that provider.
Infrastructure-as-a-Service: Current Status and Future Growth Prospects of IaaS
The Infrastructure-as-a-service segment continues to remain extremely competitive as the market base consolidates around large scale players like Amazon Web Services, Microsoft, Google and IBM.

Data collected by Synergy Group in Q3-2018 show that Amazon Web Services accounted for a lions share of the IaaS segment with 34% market share.
“Market leader Amazon maintained its dominance and remains bigger than its next four competitors combined. Its sheer scale prevents it from growing as fast as the chasing pack, but it still managed to nudge up its market share a percentage point to a little over 34%.” – SRG

Key Development: Cloud IT Infrastructure Revenue Overtakes Traditional IT Infrastructure Revenue
Research and Consulting firm IDC reported that “in 3Q18, for the first time, quarterly vendor revenues from IT infrastructure product sales into cloud environments surpassed revenues from sales into traditional IT environments, accounting for 50.9% of the total worldwide IT infrastructure vendor revenues, up from 43.6% a year ago.”
Software-as-a-Service: Current Status and Future Growth Prospects of SaaS
Software-as-a-Service, or SaaS, is a cloud-based method of delivering software applications to users. The traditional way of selling software for annual licensing fees is slowly making way for the more flexible pay-as-you-go, on-demand delivery of software. As the transition from the licensing to the subscription-based model continues, several large and niche players now operate in the SaaS market.
The key providers in the SaaS market can be divided into two subgroups: vertical and horizontal. Salesforce is a good example of a vertical SaaS provider, as it remains strong in one core area of expertise – Customer Relationship Management, or CRM. Another example is IBM Watson, which focuses on providing analytics services.
Dominant horizontal SaaS providers include companies like Oracle, who offer a wide range of products covering Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), CRM, Supply Chain Management (SCM) and Human Capital Management (HCM.) Microsoft is another horizontal SaaS provider, offering productivity tools like Office 365 and other collaborative services, as well as CRM and ERP services through Dynamics 365.
The Cloud Software market reached $72.2 billion revenue in 2018, representing a 22.7% year over year growth rate. Gartner expects cloud software market to surpass $113.1 billion by 2021 at a compound annual growth rate of 12.6%.

Data Source – Gartner, 2019, 2020 and 2021 revenue are forecasts
Microsoft is the leading SaaS provider, accounting for 17% of the market in Q2-2018. Despite being the largest player in the segment, Microsoft’s SAAS revenue grew by 45% between the second quarter of 2017 and 2018.

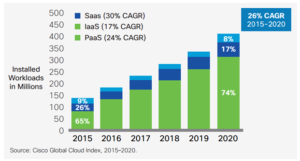 SaaS delivery will significantly outpace traditional software product delivery, growing nearly five times faster than the traditional software market and becoming a significant growth driver to all functional software markets.
SaaS delivery will significantly outpace traditional software product delivery, growing nearly five times faster than the traditional software market and becoming a significant growth driver to all functional software markets.
By 2019, the cloud software model will account for $1 of every $4.59 spent on software.” says IDC “By 2021, 75 percent of the total cloud workloads will be software-as-a-service (SaaS) workloads, up from 65 percent in 2015.” according to Cisco
Cloud Glossary
Business analytics tools
Tools that extract data from business systems and integrate it into a repository, such as a data warehouse, where it can be analysed. Analytics tools range from spreadsheets with statistical functions to sophisticated data mining and predictive modeling tools.
Business intelligence (BI) tools
Tools that process large amounts of unstructured data in books, journals, documents, health records, images, files, email, video and so forth, to help you discover meaningful trends and identify new business opportunities.
Cloud
A metaphor for a global network, first used in reference to the telephone network and now commonly used to represent the Internet.
Cloud Bursting
A configuration which is set up between a private cloud and a public cloud. If 100 percent of the resource capacity is used in a private cloud, then overflow traffic is directed to the public cloud using cloud bursting.
Cloud Computing
A delivery model for computing resources in which various servers, applications, data and other resources are integrated and provided as a service over the Internet. Resources are often virtualised.
Cloud Computing Types
There are three main cloud computing types, with additional ones evolving: software-as-a-service (SaaS) for web-based applications, infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) for Internet-based access to storage and computing power and platform-as-a-service (PaaS) that gives developers the tools to build and host Web applications.
Cloud Service Provider
A company that provides a cloud-based platform, infrastructure, application or storage services, usually for a fee.
Cloud Storage
A service that lets you store data by transferring it over the Internet or another network to an offsite storage system maintained by a third party.
Computer Grids
Groups of networked computers that act together to perform large tasks, such as analysing huge sets of data and weather modeling. Cloud computing lets you assemble and use vast computer grids for specific time periods and purposes, paying only for your usage and saving the time and expense of purchasing and deploying the necessary resources yourself. Content Delivery Network (CDN) A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a collection of global servers that caches and delivers content. It works by providing alternative server nodes for users to download resources (usually static content like images and JavaScript). These nodes spread throughout the world, therefore being geographically closer to your users, ensuring a faster response and download time of content due to reduced latency Data Center
A data center is a facility that centralizes an organization’s IT operations and equipment, and where it stores, manages, and disseminates its data. Data centers house a network’s most critical systems and are vital to the continuity of daily operations. Consequentially, the security and reliability of data centers and their information is a top priority for organizations.
Elastic Computing
The ability to dynamically provision and de-provision computer processing, memory and storage resources to meet changing demands without worrying about capacity planning and engineering for peak usage.
Hybrid Cloud
A cloud that combines public and private clouds, bound together by technology that allows data and applications to be shared between them. A hybrid cloud gives businesses greater flexibility to scale up and down and more deployment options. Hyper-scale Datacenter Hyperscale data centers have architectures that are designed to provide a single, massively scalable compute architecture. The architecture is typically made up of small, individual servers, called nodes, that provide compute, storage and networking. These nodes are then clustered together and managed as if they were a single entity. Nodes are typically deployed from inexpensive, off the shelf servers.
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS)
A virtualised computer environment delivered as a service over the Internet by a provider. Infrastructure can include servers, network equipment and software. Also called hardware as a service (HaaS).
Middleware
Software that lies between an operating system and the applications running on it. It enables communication and data management for distributed applications, like cloud-based applications, so, for example, the data in one database can be accessed through another database. Examples of middleware are web servers, application servers and content management systems.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
A computing platform (operating system and other services) delivered as a service over the Internet by a provider. An example is an application development environment that you can subscribe to and use immediately. Azure offers PaaS. Discover the advantages of PaaS.
Private Cloud
Services offered over the Internet or over a private internal network to only select users, not the general public
Public Cloud
Services offered over the public Internet and available to anyone who wants to purchase them.
Software as a service (SaaS)
An application delivered over the Internet by a provider. Also called a hosted application. The application does not have to be purchased, installed or run on users’ computers. SaaS providers were previously referred to as ASPs (application service providers).
Virtual Machine
A computer file (typically called an image) that behaves like an actual computer. Multiple virtual machines can run simultaneously on the same physical computer.
Virtualisation
The act of creating a virtual rather than a physical version of a computing environment, including computer hardware, operating system, storage devices and so forth.
Sources:
Microsoft
MaxCDN
Paloaltonetworks
Storage-switzerland
Gtmetrix
IBM